On This Page
Ayurvedic Treatment of Venom Allergy – Causes, Symptoms and More
आग्नेयैरल्पसंस्रावोदाहरागविसर्पवान् l
पक्वपीलुफलप्रख्य: खर्जूरसदृशोअथवाll
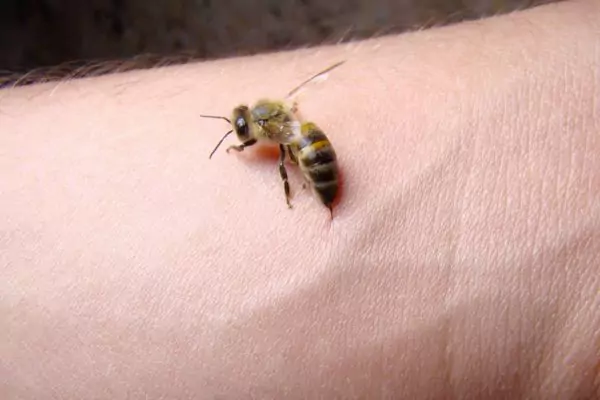
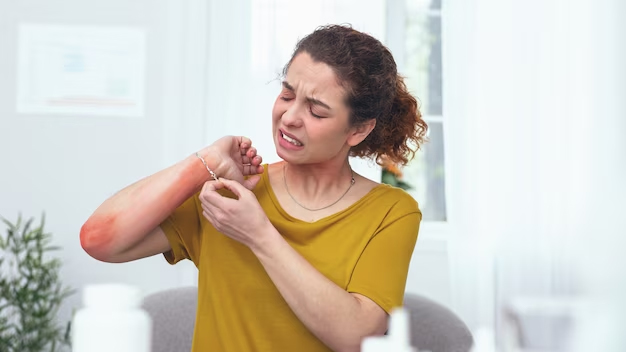
Venom allergy refers to a hypersensitive reaction by the immune system to the injected venom by some insects with stings. The allergy occurs when the immune system identifies the proteins in the venom as a threat by mistake and as a result initiates an exaggerated response. Some of the common insects that may start an allergic reaction are bees, wasps, fire ants, and yellow jackets. The symptoms of venom allergy include redness, pain, swelling at the site of insect sting to some severe systemic reactions such as difficulty in breathing or hives. Therefore, insect stings need quick Venom Allergy treatment and Ayurveda implementing natural approaches provide effective solutions to these issues.
In Ayurveda, Acharyas (teachers) mention about Keetavisha (poisoning by insects) in which symptoms and treatment of various insect bites are explained.
Causes of Venom Allergy
The venom allergy occurs from an overactive immune response to proteins present in the venom of some insects. The main causes of venom allergy are described below:-
1. Increased Sensitivity to Venom Proteins
If a person has an insect bite then the immune system reacts strongly to the proteins present in the venom. Sometimes, the first exposure can make the immune system more sensitive and respond in a hyperactive manner on subsequent bites.
2. Genetic Factors
Some individuals are more sensitive towards proteins present in the venom and exhibit a heightened allergic response due to some genetic factors.
3. Type of Insect
Different insects have different amounts of venoms for example insects like bees and wasps have higher concentration of venom that has a higher probability of initiating an allergic response.
4. Immune System Sensitivity
Some people have a sensitive immune system which makes them more prone to allergic reactions on being exposed to venom proteins. Now let’s discuss which families of insects trigger an allergic reaction.
Following are the three major families of insects that cause allergy on bite.
- Vespidae: Include insects like yellow jackets, hornets, wasps
- Apidae: Include bees like honey bees, bumblebees, sweat bees
- Formicidae: Fire ants (commonly cause Anaphylaxis), harvester ants
In Ayurveda, there is reference about various insects that bite human beings and give rise to allergic responses. They are mentioned under group Keeta and include various insects like Makshika, Kanabha, Vrischika etc. The categorization is done on the basis of dosha predominance into Vatika, Paithika, Kaphaja and Sanniptahika Keeta. The Ayurvedic texts also highlight the signs, symptoms and treatment of each of these insects’ bite.
Symptoms of Venom Allergy
The symptoms of insect sting bite allergy are as follows:
- Pain
- Redness
- Swelling (around insect bite and sometimes spread to other parts)
- Flushing
- Hives
- Itching
- Anaphylaxis: It is a serious condition that leads to difficulty in breathing and the body can also go into shock and there are a range of symptoms such as dizziness, unconsciousness, inflammation of tongue, pain during swallowing, nausea, vomiting, and low blood pressure.
Ayurveda explains the symptoms of paithika keeta as redness, burning sensation and blackish red discoloration at the site of bite.
Ayurvedic Reference of Venom Allergy (Keetavisha)

Some Facts
- Insects like fire ants, yellow jackets, hornets, and wasps can sting repeatedly. Honeybees have barbed stingers and they leave these stingers in the victim’s skin. It is best advised to remove these stingers by a scraping action instead of pulling them to avoid releasing more venom into the skin.
- Fire ant sting produces itching, hive or lump at the site which becomes better within 30-60 minutes. Then a small blister appears within 4 hours and it becomes a pus-filled cavity within 8 to 24 hours. When these lesions heal they may leave a scar behind.
- It is important to prevent secondary bacterial infection and therefore it is advised to clean the surface with soap and water and do not puncture the blister.
Also Read:- Insect Sting Allergy Treatment
Diagnosis of Venom Allergy
Diagnosis can be done by taking detailed medical history including type of exposure, previous exposure etc. Tests like skin-prick test, intradermal skin test or blood test can be performed.

“Ayurveda empowers people not only regarding life’s higher purposes but also provides profound knowledge on natural healing methods. At Dr. Gupta’s IAFA, we are enlightening the world by sharing health secrets mentioned in ancient ayurvedic texts and enable people to have improved health outcomes and improved quality of life.”
Remarkable medicine. Remarkable care!!! Dr. Gupta’s IAFA for your healthy future!!
– Dr. Sahil Gupta (B.A.M.S., M.H.A.)
Ayurvedic Allergy Specialist
CEO & Founder of IAFA®
At last, Easier Venom Allergy Management

Trusted by
More than 90,000 Patients

Convenient
at-Home Treatments

9.2 / 10
Customer Satisfaction Score
Ayurvedic Treatment of Venom Allergy
In Ayurveda, the treatment of venom allergy is advised by integrating oral medications, external applications, and detoxification procedures. This alternative and natural treatment for venom allergy prioritizes pain management, removal of toxins and prevention of complications.
Internal Medicines
The following oral medications are effective in the treatment of venom allergy but should be taken under the guidance of Ayurvedic practitioner:
- Kaishor Guggul
- Neelitulasyadi Kashaya
- Vilwadi Gulika
- Dasanga Gulika
- Lodhrasevyadi Kashaya
- Dushivisari Gulika
- Avipattikar Churna
External Medicines
External herbal remedies for venom allergies include:
- Triphala churna
- Nimbadi Churna
- Vilwadi Gulika
- Aragwadhadi Kwatham
- Guluchyadi Kwatham
Treatment Procedures
- Kashaya Dhara (Pouring medicated liquid on affected area)
- Virechana (Purgation)
- Raktamokshana (Bloodletting)
The Following Herbs are Used in Ayurveda Against Insect Bites
- Lakshmana (Biophytum Sensitivum)
- Haridra (Curcuma longa)
- Tulsi (Ocimum sanctum)
- Padmarkam (Nelumbo Nucifera)
- Lodhra (Symplocos Racemosa)
- Sirisha (Albizia Lebbeck)
- Lakshmana or Vipareeta lajjalu (Biophytum sensitivum)
Diet Management for Venom Allergy
Pathya (Do’s)
- Puffed rice
- Bitter vegetables like bitter gourd
- Green gram
- Include more fruits and vegetables
- Water boiled with Khadirasara (Acacia catechu)
- Sufficient quantity water intake
Apathya (Don’ts)
- Spicy and sour food
- Non vegetarian diet
- Day sleep
- Curd
- Excess exposure to heat and sunlight
- Heavy and fatty meal
Yoga and Pranayama in Allergy
Although yoga and pranayama does not have a direct impact on the healing of venom allergy, Yogic kriyas help to maintain the overall health and well-being and reduces the severity of allergic reactions. Moreover, it is important to elevate the part (if possible) with insect bite so that there is no accumulation of fluid and the swelling and associated symptoms can become better. Yoga and pranayama also helps to promote calmness and alleviates anxiety that also boosts the healing process and helps the individual to get rid of these annoying symptoms with a positive frame of mind and assist in natural treatment of venom allergy.

Frequently Asked Questions
Question: Which are the Common Insects that Cause Allergy on Bite?
Answer: Common insects causing allergy are Yellow Jackets, Honey bees, Fire ants etc.
Question: When Does Insect Bite Allergy or Venom Allergy Need Immediate Care?
Answer: If individuals experience symptoms like dizziness, nausea, vomiting, unconsciousness, and low blood pressure etc. Then it represents anaphylaxis reaction and should be managed under emergency care.
Question: What is Ayurvedic Management in Venom Allergy?
Answer: Allergic reactions caused by insect sting can be treated effectively by Ayurvedic medicines. It includes internal as well as external medicines along with detoxification therapies.
References
- Shloka No. 2, Keetaluthadivisha Prathishedha, Ashtangahrudayam by Acharya Vagbhata, Uttarasthanam.
- Ambikadutt Shastri, Sushruta Samhita, 12th ed. Chaukhambha Publication, New Delhi, 2001. p. 64.
- Ashtang Hridya, Atrideva Gupt, Reprint. Chaukhambha Prakashan, 2009.
- Charak. Charak Samhita by Dr. Brahmanand Tripathi, Reprint. Chaukhambha Prakashan. 2009.
- Ayurveda Dipika. Commentary on Charak Samhita. Chikitsasthana. 23/152, 5th ed. New Delhi: Munshiram Manoharlal Publishers Pvt. Ltd; 1992. p. 503.
- Sahil Gupta, Ayurvedic Aspects of Allergies and Fungal Infections, Edition 2021, Insect Sting Allergy Chapter No. 04, Page No. 28-33.
Dr. Gupta at IAFA is an experienced Ayurvedic Practitioner spreading awareness about Ayurveda in different parts of the world. Dr. Gupta’s IAFA is a leading institute that provides 100% natural and holistic treatment for all the types of allergies including venom allergy.
“Experience the extraordinary only at IAFA.”
Was this Page Helpful?
So IAFA Root-Cause Treatment of Your Venom Allergy in Ear is Just 3 Steps Away!

01. Connect With Us
Share your history of illness or Book your appointment

02. Consult With Us
Dr. Gupta a certified Ayurvedic Allergist Consultant

03. Root Cause Treatment
Get an accurate diagnosis, medicines, diet & lifestyle change
Venom Allergy – Case Studies
Real Case Studies of Successfully Treated Patients from All Around the World by IAFA Ayurveda®
-

Successful Treatment of Pityriasis Alba and Allergy March in Ayurveda – A Case Study
It is a case study about successful treatment of Pityriasis Alba and…
-

Successful Treatment of Gallstones (Cholelithiasis) with Ayurvedic Medications – A Case Study
It is a case study about the successful treatment of Gallstones (Cholelithiasis)…
-

48-Year-Old Male Patient Got Relief from Chronic Aspergillosis of Paranasal Sinuses – A Case Study
Fungal infections can be treated with a high success rate by various…
-

6-Year-Old Child Patient Got Relief from Gluten Intolerance and Wheat Allergy – A Case Study
It is a case study of a 6-year-old Child Patient who got…