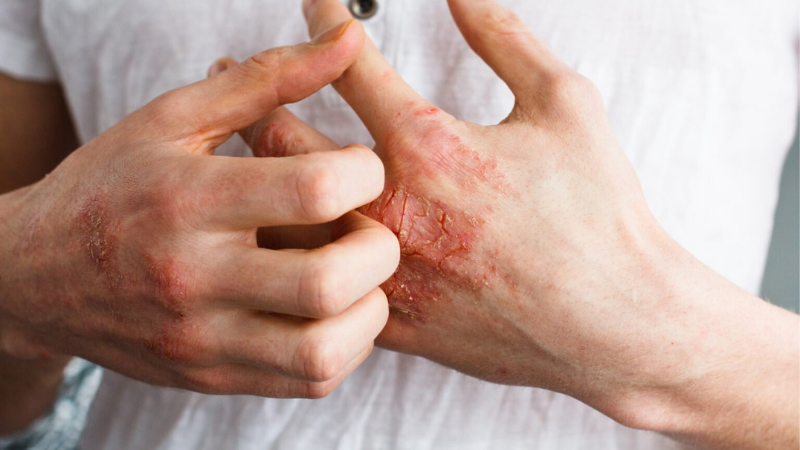
Eczema often disturbs your daily life. The constant itching can give you sleepless nights, the flare-ups can make it difficult to focus on your work, and the visible patches may cause embarrassment and lower your confidence.
If you are relying on steroid creams or antihistamines, you already know they may calm symptoms for a while, but the moment you stop, the disease recurs. That’s because they don’t fix the root cause.
This ongoing struggle leaves you tired, frustrated, and looking for a permanent solution.
Ayurveda, on the other hand, dives deeper.
Ayurveda considers eczema (Vicharchika) not just a skin problem but an outcome of dosha imbalance, weak digestion, and toxin buildup inside the body.
Ayurveda helps you in permanently treat your eczema by correcting these root issues with herbs, diet, and lifestyle changes. Let’s discuss what causes eczema, ayurvedic medicine for eczema, and other important factors in detail.
What Causes Eczema?
You can suffer from Eczema, or Vicharchika, if you have an imbalance of all three doshas, but majorly the Kapha and Pitta doshas. These imbalances lead to weakened digestive fire (Agni) and increase toxins (Ama) that create Rakta doshas in your body.
These imbalances in doshas, along with Rakta Doshas, happen because of different causes like Dietary causes (Aharaja Nidana) and others that I am discussing below –
1. Aharaja Nidana (Dietary Causes)
Aharaja Nidana means dietary causes that lead to disease manifestation in your body.
- Consuming Guru Ahara (heavy-to-digest food) and Snigdha (oily) Ahara in excess burdens your digestive system.
- Excessive intake of below foods also adds to the imbalance of doshas.
- Drava (liquid) Ahara like cold drinks,
- Madhura (sweet),
- Amla (sour),
- Lavana (salty)
- Katu (pungent) Ahara
- Following Mithya Ahara (improper dietary habits) for a long time weakens the digestion.
Other bad eating habits that also lead to eczema are –
- Asatmya food- Eating food not suitable for your body
- Viruddha Ahara- Incompatible food combinations, such as Heated honey, honey with hot water, fish with milk, milk with salty food, and milk with sour food.
- Pramita Bhojan- Includes irregular meals, overeating, or fasting extremes.
- Adhyashana- Having a meal before the previous one is digested. Adhyashana leads to toxin formation.
Your lifestyle is just as important as your diet. Some habits that silently fuel eczema are –
- Staying awake at night (Ratri Jagrana) disturbs both Vata and Pitta doshas.
- Sleeping during the day (Diva Swapna) increases Kapha and leads to eczema symptoms like oozing and itching.
- Exposure to extreme cold (Ati- Sheeta), humid and hot environment (Ati-Ushana Sevana)
- A sedentary lifestyle (Alasya or Sukumarta) slows down your metabolism and increases Kapha in your body.
- Overexertion (Ati-Vyayama) dehydrates your body, which leads to scaling and cracks on your skin.
- Suppressing natural urges (Vega Dharana), especially vomiting or urination, disturbs energy channels in your body and accelerates toxin formation.
3. Mansika Nidana (Psychological Causes)
Your emotions leave a direct imprint on your skin. If you are in a stressful state of mind for a prolonged time, that may cause eczema.
Various stressful states that can cause eczema are –
- Shoka (grief)
- Chinta (worry)
- Krodha (anger)
These mental states disturb Pitta and Vata doshas, causing itching, redness, or worsening dryness on your skin.
4. Anya Nidana (Other Causes)
Sometimes you are not aware of the cause, but it still plays a crucial role in your eczema. These are –
- Bija Dosha (hereditary causes)- health tendencies passed down through family genes, like the filaggrin mutation.
- Krimija Nidana- changes in skin microbiome or gut bacteria imbalance leading to eczema flare-ups.
- Rakta Dushti- impure blood acting as the medium for dosha imbalance to manifest as eczema on your skin.
Ayurvedic Herbal Medicine For Eczema
1. Guduchi (Tinospora Cordifolia)

Guduchi (commonly known as Giloy) is a popular immunity-building herb because it helps in increasing white blood cells that fight infections in the body.
Giloy is a primary herb used in the treatment of dengue or chikungunya in Asian countries like India.
Guduchi works as the best Rasayana Dravya in eczema treatment because the herb has not only Kapha and Pitta pacifying properties, Rakta Prasadna (blood purifying) properties.
Giloye helps in reducing Kandu (itching), Strava (oozing), and Daha (inflammation), which helps in healing eczema.
Modern studies also support Guduchi’s benefits because Guduchi has active compounds like tinosporaside, cordiofolioside A & B, columbin, and tinosporin that suppress inflammatory pathways (TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, and NF-κB).
This helps reduce chronic skin inflammation.
Guduchi also contains berberine-like alkaloids having antimicrobial and antifungal properties that protect your skin from the recurrence of eczema.
How to use
#1. Internal use
You can consume Giloye as a Kashaya (decoction) 10- 20 ml/day or Churna (powder) 3–6 g/day.
#2. External use
- You can apply Giloye as Lepa (paste) or Taila (Ayurvedic formulated oil) to soothe lesions.
- Make a paste with Ghrita (Ghee) and Haridra or neem, then apply it to the skin.
Precautions
- Avoid consuming if suffering from liver disorders such as Jaundice.
- Avoid in pregnancy and breastfeeding
- Consult an Ayurvedic doctor for using Guduchi if you are on immunosuppressant medicines.
Side effects
- Giloye may cause stomach upset, nausea, and mild gastritis on excessive usage.
2. Manjistha (Rubia Cordifolia)
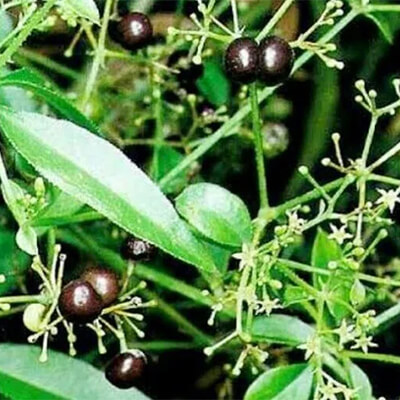

Manjistha, used in Rakta shodan, removes toxins from the body and helps in balancing Pitta and Kapha Dosha.
Manjistha herb contains alizarin, rubiadin, purpurin, and phenolic compounds, which reduce skin inflammation, mitigate free radicals to reduce skin damage, and cure eczema lesions.
The herb also speeds up epithelialization (dark hard skin layer that covers the wound during the healing process) and collagen synthesis by its anti-pruritic and wound healing activity.
How to use
#1. Internal use
You can use Churna (powder) around 3–6 g/day.
Consume Kwath (decoction) up to 30- 40 ml twice a day or as per the severity of the condition.
You can also consume formulations, like Ghrita and Avleha, after consulting the expert.
#2. External use
You can also use Manjistha externally in Taila (oil) form to reduce itching, redness, and oozing. Take Manjistha and Gulaab Arka (Rose exilir) to form Lepa (paste). Apply the paste to the eczema site.
If you are suffering from chronic dry eczema, you can mix the herb with Narikel taila (Coconut oil) and Ghrita Kumari (Aloe vera), then apply it to the skin.
Precautions
- Avoid consuming during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
- Avoid if you have a Pitta-Dominant Prakriti or use under doctor’s supervision
- Avoid in renal dysfunction
Side effects
- Gastritis and hyperacidity in a Pitta-dominant person
3. Khadira (Acacia Catechu)
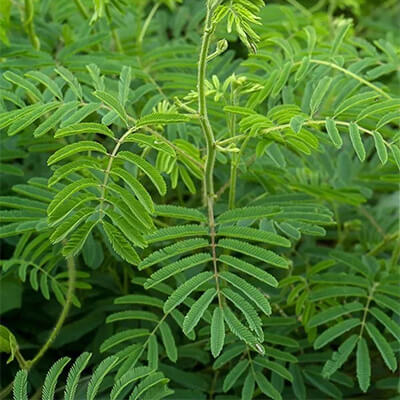

Khadira is considered Agrya Dravya (Superior herb) for skin disorders.
You can use Khadira for Rakta Shodhaka (blood purifier), Kandughna (anti-pruritic), Sithhara (anti-inflammatory), and Daha Prashamaka (reduces burning sensation).
Thanks to its Kashaya Rasa (astringent), Tikta Rasa (bitter), and cold potency (Sheeta Virya) properties, it acts best for these imbalances and purifies the blood.
As per modern science, Khadira contains key phytochemicals, like catechin, isoflavonoids, tannins, quercetin, and kaempferol, which help inhibit inflammatory mediators, prevent secondary infection in eczema, reduce oozing, weeping eczema, and itching.
The herb also helps in enhancing collagen cross-linking and skin tightening properties that not only heal the eczema, but also rejuvenate the skin.
How to use
#1. Internal use
- Consume 15- 20 ml daily of Khadira either as a Kwath (decoction) or Arishta (water or alcohol soluble), which is very effective in chronic eczema.
- Take 3–6 g/day of Churna (powder) with water
#2. External use
- Apply as a Lepa (paste) after mixing with Ghrita Kumari (aloe vera) and Narikela Taila (coconut oil).
- Use its Kwath (decoction) for Snana (Bathing) and for washing the eczema patches.
Precautions
- Not recommended during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
- Avoid if you have severe Vata-Parkopa or consult a doctor if he allows with Ghrita or Taila.
- Avoid if you have severe Ruksta (dryness).
Side effects
- Constipation
4. Haridra (Curcuma longa)

Haridra (turmeric) is a natural cleanser and healer for stubborn skin conditions like eczema. Because of its skin nourishing properties, like –
- Krmighana (antimicrobial)
- Kusthaghna (antidermatosis)
- Kleda Soshana (anti-inflammatory)
Haridra (commonly known as haldi) is a Pitta-Kapha pacifier because of its Tikta (bitter), Katu (pungent) Rasa, Ushna Virya (hot potency), and Laghu (light), Ruksha (dry) qualities.
Turmeric purifies & strengthens blood (Rakta Dhatu Dushti) by its Rakta Shodhaka Karma & rejuvenates the skin by Twachya Karma.
Curcuma Longa possesses key phytochemicals like curcumin, bisdemethoxycurcumin, and turmerone. These antioxidants exhibit anti-inflammatory and anti-microbial properties.
Haridra enhances the skin lipid layer and restores the barrier in chronic eczema. The best part is that Haridra also promotes collagen synthesis and heals the lesions.
How to use
#1. Internal use
- Golden Milk – You should consume Haridra with milk (popular as golden milk), which is classically used for immunity and blood purification.
- Take Churna (powder) 2- 3 g twice a day.
#2. External use
- Mix with coconut oil and use a medicated oil on the skin.
- Apply as a Lepa (paste) after mixing with Ghrita Kumari (aloe vera) and Narikela Taila (coconut oil) on local patches of eczema.
- Use Kwath (decoction) for cleaning lesions.
Precautions
- Avoid during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
- Avoid in bleeding disorders because it may cause blood thinning if consumed in high doses.
Side effects
- May cause a burning sensation and acidity if you are a Pitta-sensitive person.
- Acts as a blood thinner if used excessively.
5. Amalaki (Phyllanthus emblica)

In Ayurveda, Amalaki, or Amla, is called the best rejuvenator because Amalaki carries all tastes (Rasas) except salty (Lavana), making it a versatile herb.
A herb’s taste defines its effectiveness in balancing the tri-doshas in your body. These tri-doshas are Vata, Pitta, and Kapha.
Amalaki is highly effective in calming two major players in eczema –
- Pitta dosha
- Disturbed Rakta Dhatu
Thanks to its Sheeta Virya (cooling potency) and Madhura Vipaka, a sweet post-digestive effect that nourishes the body and strengthens the immunity.
Along with strengthening immunity, Amla also helps in preventing the recurrence of eczema by working as a Rakta Shodhaka (blood purifier).
Amalaki clears impurities from your body and pacifies itching, redness, and eruptions.
On the scientific side, Amla is rich in ascorbic acid (Vitamin C), emblicanin A & B, ellagic acid, and gallic acid.
These compounds shield your skin from oxidative stress, fight off secondary infections, support collagen production, and even reduce histamine release. That’s what makes Amalaki a holistic medicine for eczema.
How to use
#1. Internal use
Its Churna (powder) is recommended 3- 5 g daily with Sakoshna Jala (lukewarm water).
In eczema, it is best to use it as Triphala, i.e., in combination with Haritaki and Bibhitaki.
#2. External use
- Use Kwath (decoction)for washing eczema patches.
- Use Amalaki Churna (powder), Lepa (paste) with Ghrita Kumari (Aloe vera) on the lesion.
Precautions
- Consult a doctor before using Amalaki if you are using Anticoagulant medicine because of the interaction of ascorbic acid and tannins with the medicine.
- Avoid using it with Taila and Ghrita because of its Ruksha Guna, which may increase Vata.
- Diabetic patients should use Amalaki under medical supervision because of the risk of hypoglycemia.
Side effects
- Gastric irritation in sensitive individuals at high dosages.
6. Sariva (Hemidesmus indicus)
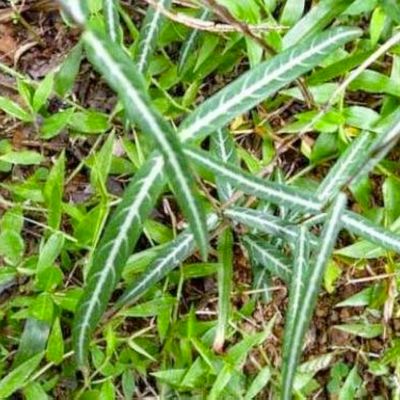

Sariva is a herb that exhibits Tridoshaghna properties, especially Pitta-Kapha Shamaka.
With its Madhura (sweet), Katu (pungent), Tikta (bitter) Rasa (taste), it reduces inflammation and burning sensation caused by Pitta Dosha vitiation.
The herb reduces skin eruption and discoloration by purifying the Rakta Dhatu.
Sariva also pacifies Kapha in your body, which helps in reducing itching and oozing in eczema.
Sariva contains coumarins, hemidesmin, and sponins, which reduce eczema-related inflammation, prevent skin cell damage, and also regulate the hypersensitive immune response, useful in atopic dermatitis.
How to use
#1. Internal use
- Kwath and Arista are used for blood purification after food, 20- 30 ml twice daily.
- Take 3- 5 g of Churna (powder) daily with Madhu (honey).
#2. External use
- Use Kalka (thick paste) with Narikela Taila (coconut oil) and rose water over eczema lesions.
- Apply Sariva Siddha Taila on dry and itchy lesions.
- Clean the oozing eczema part with Sariva Kwatha (decoction).
Precautions
- Avoid if you have an extreme cold constitution (Sheeta Guna), because Sariva (due to Vata Prakriti) may aggravate Sheeta Guna, ultimately Vata, and lead to indigestion.
- Avoid in Mandagni (low digestive fire).
- Generally safe in pregnant and lactating mothers in small doses, but consume under medical supervision.
Side effects
- Reduced appetite, mild nausea if used in excess.
7. Shatavari (Asparagus racemosus)
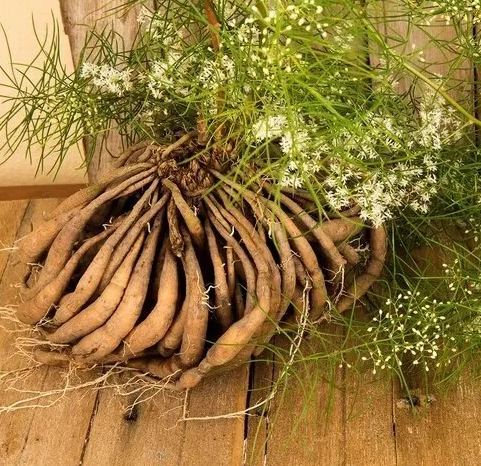

Shatavari, with its Sheeta Virya (cold potency), Madhura (sweet), Tikta (bitter), Rsaa, and Guru (heavy), Snigdha (oily) Guna, reduces burning, erythema, and irritation in Vicharchika (eczema).
You can use shatavari to nourish Rakta Dhatu and restore skin integrity.
Shatavari can help you in the healing of chronic lesions because of its Snigdha Guna, which results in reducing excessive dryness and scaling of the skin.
The herb contains key phytochemicals, such as racemosol, asparagamine, alkaloids, isoflavones, and shatavarins.
These antioxidants help in preventing chronic skin damage, reducing eczema inflammation, and healing eczematous lesions by promoting fibroblast proliferation and collagen synthesis.
How to use
#1. Internal use
- Use Shatavari Ghrita in Pita-dominant eczema.
- Consume Churna (powder) around 3- 6 g daily with Dugadh (milk) once or twice daily.
- Use Kwath (decoction) in a 20- 30 ml dosage daily.
#2. External use
- Use Kalka (thick paste) with Ghrita (Clarified butter) on dry and scaly lesions.
- Use Shatavari Ghrita on dry and itchy eczema.
- Wash oozing eczema with Shatavari Kwatha (decoction) to soothe burning sensations and reduce redness.
Precautions
- Avoid in Kapha-dominant conditions, as it may worsen the condition, like oozing because of its Snigdha and Guru Guna.
- Allowed in Pregnancy and lactation, but if eczema, then use under medical supervision.
Side effects
- Mild bloating and loose stool may occur if Shatavari is overused.
- May cause heaviness in the stomach if you have sluggish digestion or Mandagni.
8. Nimba (Azadirachta indica)

Nimba or Neem acts very well as Rakta Shodhaka (blood purifier) as it has Tikat (bitter), Kashaya (astringent) Rasa with cold potency and Laghu (light) and Ruksha (dry) Guna.
Nimba calms Pitta and reduces inflammation, redness, and burning sensation, thanks to its Sheeta Virya (Cooling properties) and Tikta Rasa (Bitter taste).
Nimba reduces Kapha in your body and dry oozing lesions because of its Kashaya Rasa and Ruksha Gunas.
Neem activates in Rkata Shodhaka Karma (blood purification), removing all the toxins that contribute to eczema.
Neem possesses phytochemicals such as nimbidin, quercetin, gedunin, and flavonoids, which reduce irritation, redness, and swelling associated with eczema.
Nimba prevents secondary infection in eczema, with its anti-microbial properties.
You can also get relief from chronic eczema lesions, because Nimba enhances keratinocyte proliferation and collagen disruption that accelerates skin cell repair.
How to use
#1. Internal use
- Churna (powder) is recommended 2- 4 g daily with Sakoshna Jala (lukewarm water)
- Consume 20-30 ml of Kwath (decoction) in inflamed eczema or oozing eczema.
#2. External use
- Use pure Neem oil to reduce itching, microbial infection, and scaling.
- Apply Neem leaves paste (Kalka) on eczema patches.
Precautions
- Avoid in Ruksha Vicharchika lesion (dry eczema)or use in combination with oil or Ghrita.
- Avoid consuming in weak digestion or low body weight, as it may deplete weight faster.
- Avoid in pregnancy
- Nimba oil ingestion can be toxic in children. Keep out of reach of kids.
Side effects
- May cause hypoglycemia and nausea.
- Irritation on exposed skin..
9. Other Herbs Effective in Eczema
You can use several other herbs that are also effective in eczema control and skin rejuvenation. Some of the important herbs are –
- Bhringraja (Eclipta alba)
- Kutaja (Holarrhena antidysenterica)
- Karanja (Pongamia pinnata)
- Daru-haridra (Berberis aristata)
- Bakuchi (Psoralea corylifolia)
- Snuhi (Euphorbia neriifolia)
- Shirish (Albizia lebbeck)
You can use the above-discussed herbs for managing eczema at home, but if you are looking for a more holistic and long-lasting solution, then explore effective Ayurvedic formulations, discussed in the next section.
Read our detailed case study – 40-Year-Old Female Patient Recovered from Dyshidrotic Eczema and Onychomycosis
Classical Ayurvedic Formulations (Holistic) Medicines for Eczema
1. Rakta Karavira Taila
Rakta Karavira Taila acts on Tridosha but primarily balances Kapha and Pitta in your body. The oil contains cardiac glycosides, including oleandrin, which has antimicrobial, antifungal, and keratolytic properties.
Karavira, in the oil, botanically known as Nerium indicum, is Krimighna (antiparasitic), Kusthghna (skin disease alleviating), and Daha Shamaka (burning sensation relieving) Dravya that reduces infection, and soothes the skin.
When you apply Taila (oil) on the problematic area, it reduces Kandu (itching), Paka (oozing), and softens chronic plaques.
How to use
You can use externally on chronic eczematous patches or use as a base in various Lepa (paste) with other herbs (mentioned previously) as prescribed by the doctor.
Precautions
- Karvira is toxic internally, so do not ingest.
- Never apply Karvira to fresh oozing lesions, mucous membranes, or open wounds.
- Avoid its use in children and pregnant women.
2. Sariva Arishta (Fermented decoction preparation of Hemidesmus indicus)
Sariva is a popular herb that acts as a Kusthaghna (skin disease reliever), Rakta Shodhaka (blood purifier), and Daha Shamaka (reliever of burning sensations).
You can improve your metabolism and digestion by consuming the fermented decoction of Sariva.
Sariva Arishta contains hemidesmin, saponins, and tannins. These phytochemicals reduce inflammatory reaction in eczema, with their anti-inflammatory, immunomodulatory, antioxidant, and hepatoprotective qualities.
How to use
Internal use
- Consume 15–30 ml with an equal amount of water after meals, 2 to 3 times daily under medical supervision.
Precautions
- Avoid if you have gastric irritation or alcohol sensitivity.
- Avoid in children.
3. Panchanimba Churna
Panchnimba is the best ayurvedic medicine for eczema.
Panchnimba Churna is a combination of five parts of Neem along with Trikatu, Chitraka, Triphala, and others. The churna helps in balancing Pitta-Kapha in your body and also acts as Krimighna (antimicrobial) and Kushtaghna (antipruritic).
Neem has active ingredients like azadirachtin and nimbidin, which possess antimicrobial, antifungal, and anti-inflammatory properties, which give excellent results in eczema.
How to use
- Consume 3–6 g of Panchanimba Churna with warm water twice daily.
Precautions
- Avoid during pregnancy, gas trouble, diarrhea, or excessive dryness.
4. Khadirarishta
Khadirarishta contains Khadira (Acacia catechu) that purifies blood, calms Kapha-Pitta, and reduces inflammation.
Khadira possesses various catechins, quercetin, and tannins with anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and antimicrobial activity, which heal eczema efficiently.
Khadira Arista is the best Kusthghna formulation, which is Kapha-Pitta Shamaka, and Rakta Shodhaka (blood purifier).
How to use
- Take 15–25 ml of Khadira Arishta after meals with an equal amount of water, twice daily.
Precautions
- Avoid if you have gastric irritation or alcohol sensitivity.
5. Rasa Manikya
Rasa Manikya is a purified mineral formulation of the arsenic trisulfide as mentioned in Rasa Shastra.
Manikya Bhasma shows strong antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, and immunity-boosting effects, making it highly effective in controlling eczema.
Rasa Manikya also supports digestion and metabolism (Deepana–Pachana), while purifying the blood (Rakta Shodhana). This blood-cleansing action is vital because Rakta Dushti (vitiation of blood) is the root cause of eczema in Ayurveda.
How to use
- You can consume 30–125 mg with honey, ghee, or decoction. You can also combine with other formulations like Gandhaka Rasayana or Khadirarishta.
Precautions
- High doses can be toxic. Use under Ayurvedic physician supervision.
- Avoid in children, pregnant women, and patients with liver or kidney disorders.
6. Panchtikta Ghrita Guggulu
In Panchatikta Ghrita Guggulu, bitter herbs (Tikta Dravyas) are formulated with Ghrita (clarified butter), which helps cool excess heat (Pitta) and cleanse the blood.
Guggulu contains guggulsterones, which act as Shothahara (anti-inflammatory) that reduces swelling and irritation in eczema.
How to use
- 1–2 tablets twice daily with lukewarm water (Sakoshan Jala). Chew before swallowing for better results.
Precautions
- Avoid in hyperthyroidism and gastritis.
7. Arogyavardhini Vati
Arogyavardhini Vati acts as Yakrit-Uttejaka, a liver stimulant, Deepana (appetizer), and Rakta Shodhaka (blood purifier), which helps in clearing vitiated Pitta from your blood.
Arogyavardhini Vati contains various herbs like Kutki and Triphala that help in improving liver function, detoxification, and skin health.
How to use
- 1–2 tablets twice daily with water.
Precautions
- Avoid in severe liver impairment or in children without expert supervision.
8. Gandhaka Rasayana
Gandhaka Rasayana is prepared from Suddha Gandhaka (purified sulfur).
Gandhaka Rasayana acts as Rasayana (rejuvenator), Kusthaghna, and most importantly, Vrana Shodhana (wound cleansing).
Sulfur compounds have anti-fungal, anti-bacterial, and keratolytic effects that work similarly to topical sulfur used in modern dermatology for eczema.
How to use
- 250–500 mg with milk, ghee, or honey on a divided basis daily.
- Ointment is also available for topical use.
Precautions
- Only safe if properly purified and taken in the right dose as per the doctor.
- Overuse can upset your stomach or cause headaches.
9. Other Classical Formulations
Your doctor may also suggest Panch Tikta Kwatha, Nimbadi Kwath, Khadiravaleha, Panchatikta Ghrita Avaleha, Triphala Churna, Shirish Aasava, Mahamanjisthadi Taila, and Maha Manjisthadi Kwatha, which are highly effective in eczema and skin issues.
Read – Case study of a young male patient who recovered from Eczema and Seborrheic Dermatitis
Lifestyle & Diet Recommendations in Ayurveda For Eczema
1. Foods to Include (Pathya)
You can consume below mentioned foods for quicker results in eczema healing.
- Laghu Anna (light food articles to digest)
- Tikta Shaaka (bitter vegetables)
- Purana Dhaanya (old cereals & grains)
- Jaangala Maamsa (unsaturated animal fat)
- Mudga (greengram)
- Patola (snake guard)
- Mudga (greengram)
- Purana Shaali (old, stored rice)
- Yava (Barley grain)
- Shashtika Shaali (variety of rice explained in Ayurveda)
- Godhuma (wheat grain)
- Food and ghee prepared by Triphala & Nimba
- Khadira Jala Pana (Drink prepared from the extraction of the Acacia catechu plant)
- Aushadha Sanskrita Takra (medicated buttermilk)
2. Foods to Avoid (Apathaya)
Avoid below mentioned foods for better results in eczema healing.
- Navanna (newly formed rice)
- Guru Anna (heavily digestible foods)
- Amla Rasa (citrus fruits)
- Dugdha (She-buffalo milk)
- Dadhi (curd)
- Matsya (fish)
- Guda (jaggery)
- Tila Taila (unrefined sesame oil)
- Kulattha (Horse gram)
- Masha (black gram)
- Nishpava (field beans)
- Ikshu pishta (food articles, i.e., sweets prepared with sugar)
- PishtaVikar (carbohydrate-rich foods)
3. Viruddha Ahara (Incompatible Food Combinations)
Avoid food combinations like
- Fish with Milk
- Gramya, Anupa, or Audaka Mamsa with Milk
- A diet containing cereals like Yavaka, Chanaka, Udalaka, Kodrava, Kulattha, Kola, Masha, Atasi, or Kusumbha with milk, curd, and butter milk
4. Lifestyle Habits to Include
- Karanja Taila Abhyanga (massage with Pongamia pinnata oil)
- Parisheka (medicated bath in which water is sprinkled on the body)
- Avagaha (bath) with Khadira Kashaya (Acacia catechu plant
- Brahmacharya (abstinence from sexual activities)
- Mukha Prakshalana (face cleaning)
- Ardha Bala Shakti Vyayama, i.e., half strength exercise, should be done daily.
- Ritucharya: One should observe and follow the seasonal regimen
5. Lifestyle Habits to Avoid
- Eating at irregular times (Vishamashana) or not following proper food conduct (Mithya Ahara).
- Divasvapna (day sleep)
- Maithuna (sexual intercourse)
- Vegadhaarana (suppressing the natural urge of the body)
- Paapakarma (sinful acts)
- Uccha Vachan (loud speaking) Varjana
- Tapa sevana (excessive exposure to sun rays)
- Swedana (fomentation)
- Ati-Shoka (excessive grief)
- Ati Vyayama (excessive physical exercise)
- Hima Aatap (exposure to excessive heat or cold) Varjana
- Pravaata (walking in open air) Varjana
- Yaanadhwa (journey or excessive walking) Varjana
- Dhuma-Rajasi (fume and dust) Varjana
- Raatri Jagrana (night awakening) Varjana.
Benefits of Choosing Ayurveda for Eczema
Ayurveda works on the root cause by balancing doshas like Vata, Pitta, and Kapha. Whereas the other branches of medicine primary work on the symptoms.
Let’s discuss how Ayurveda is better in treating eczema compared to other medical branches.
1) Ayurveda Vs Allopathy
Whereas modern medicine mostly manages eczema with steroid creams and strong immunosuppressants like cyclosporine or methotrexate.
You may find a quick reduction in itching and redness, but these medicines don’t touch the root cause. With long-term use, you get unwanted side effects such as skin thinning, dependency, lowered immunity, and even damage to your liver or kidneys.
2) Ayurveda Vs Homeopathy
Homeopathy brings an alternative medicine for eczema without any side effects. Homeopathy works on the principle of cure by prescribing small doses based on symptoms.
It may provide temporary relief in some cases, but it lacks dietary and lifestyle modification as per the Dosha involved.
Homopathy’s effectiveness is variable, less predictable, and not strongly validated by clinical trials in the case of eczema treatment.
3) Ayurveda Vs Alternative Treatments
Other therapies like naturopathy, yoga, and diet-only methods work mainly on lifestyle correction and external soothing, which includes oils and packs.
Though these therapies may reduce symptoms, but often lack main pathogenesis correction, thus providing temporary relief.
Alternative therapies work best if combined with Ayurveda and speed up the recovery.
4) Why is Ayurveda Safer?
Ayurveda doesn’t suppress the symptoms but works on the root cause for complete healing.
In Ayurveda, eczema (Vicharchika) is a result of Kapha, Pitta, and Rakta imbalance, coupled with weak Agni (digestion) and disturbed immunity.
When you use herbs like Guduchi, Manjistha, Neem, Haridra, and Sariva. These herbs purify blood, modulate immunity, reduce inflammation, and restore digestive fire.
Panchakarma therapies go even deeper, flushing out toxins from the root. Best of all, when used correctly, Ayurvedic medicines don’t cause long-term organ toxicity or dependency, which is a common concern in Allopathy.
The best part is that Ayurveda always provides personalized treatment based on your Prakriti (constitution), dosha involvement, and causative factors.
Along with medicines, you also get clear Apathya-Ahara (dietary rules) and lifestyle guidelines to prevent recurrence.
How Long Does Ayurvedic Treatment Take for Eczema?
Your eczema recovery depends on the severity of the disease. Different eczema stages based on the severity and their duration of treatment are discussed below –
1) Mild Eczema
Where eczema is in the initial stage or mild eczema like Dyshidrotic Eczema, with localized patches and occasional itching –
- 1-2 months for proper relief
- 3-4 months for the prevention of recurrence.
- With a strict diet & disciplined lifestyle, results may come in just 3–6 weeks.
2) Moderate Eczema
Where eczema is in a chronic stage, recurrent, wider spread, with oozing from the affected area.
- Major improvement after 3-6 months of continuous treatment
- 6-9 months for long-term remission of the eczema
- Pathya (dietary and lifestyle) discipline speeds up recovery
- Rasayana (rejuvenation therapy) prevents the recurrence of eczema
3) Severe Eczema
When eczema is very chronic, widespread, and with intense itching, the risk of secondary infection increases. Over time, it also affects your mental well-being.
- Significant disease control and skin healing may take 6–12 months.
- Maintenance therapy is continued in resistant cases.
Remember
- Pathya-Apathya Aahara and Vihara, i.e., dietary and lifestyle modification, can speed up recovery very fast.
- Use of Virrudha Aahara (Incompatible foods) worsens eczema and delays healing.
- Yoga, pranayama, and meditation also help in reducing flare-ups.
When to Consult a Doctor?
Don’t wait if your eczema takes a serious turn. Consult immediately when –
- You see pus-filled blisters, swelling, or severe redness.
- Itching and pain are unbearable, or eczema suddenly spreads over large areas.
- There is pain with bleeding skin.
- If you face difficulty breathing, chest tightness, or eye involvement (swelling, redness, blurred vision), immediately consult a doctor.
- Your home remedies haven’t worked even after 2 months.
At such times, a timely Ayurvedic consultation ensures you are moving toward long-term healing.
If you are also suffering from eczema and fed up with the recurrence of this itchy disease, you can contact IAFA, where Dr Sahil can help you heal your eczema effectively.
Dr. Sahil has 15+ years of experience in allergy and eczema cases, and his dedicated team will also help you improve your diet and lifestyle for a speedy recovery without any recurrence of disease.

Frequently Asked Questions
Que 1. What is the best medicine for eczema?
Ans. Medicines using herbs like Guduchi, Manjistha, Neem, Haridra, Sariva, Khadira, Amalaki, and Shatavari are best for eczema cure. Ayurveda offers medicine based on your dosha and symptoms that varies from person to person.
Que 2. Are Ayurvedic medicines safe for children with eczema?
Ans. Yes, but always consult an Ayurvedic doctor before giving any Ayurvedic formulation to your child.
Que 3. What specific herbs does Ayurveda recommend for reducing eczema inflammation?
Ans. Guduchi, Manjistha, Haridra (turmeric), Neem, Sariva, Shatavari, Khadira, and Amalaki reduce eczema by purifying blood, calming Pitta-Kapha, and supporting skin healing.
Que 4. How do Ayurvedic treatments compare with steroid creams for eczema?
Ans. Steroids mainly suppress the disease symptoms for short-term relief. But Ayurveda works on root causes (dosha balance, Agni, Rakta Shodhan) for longer-lasting healing.
Que 5.How can I safely combine Ayurvedic herbs with my current eczema meds?
Ans. Consult your Ayurvedic and Allopathic doctors before starting any Ayurvedic herb.
Que 6. What are the risks of using coconut oil or tea tree oil on eczema?
Ans. Coconut oil may worsen oozing Kapha-type lesions, whereas tea tree oil can trigger contact dermatitis. Always do a patch test and use only under an expert’s guidance.
Que 7. Can Ayurveda medicines cure eczema permanently?
Ans. Yes. Ayurveda aims for long-term remission by removing triggers and balancing doshas. However, relapses can occur if diet, stress, or lifestyle triggers persist.
Que 8. Is Panchakarma effective for eczema?
Ans. Yes. Panchakarma helps detoxify and balance doshas in moderate to chronic cases.